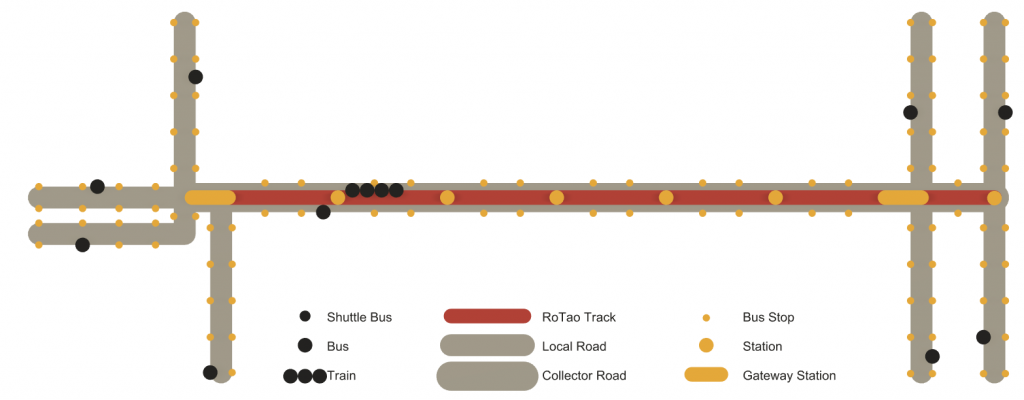
A complete Rotao hybrid public transit consists of a Metro system and feeders. The Metro system includes 2 speed levels: Rapid trains and Express trains. The feeders are surficial buses: Collector buses, local buses and optional shuttles.
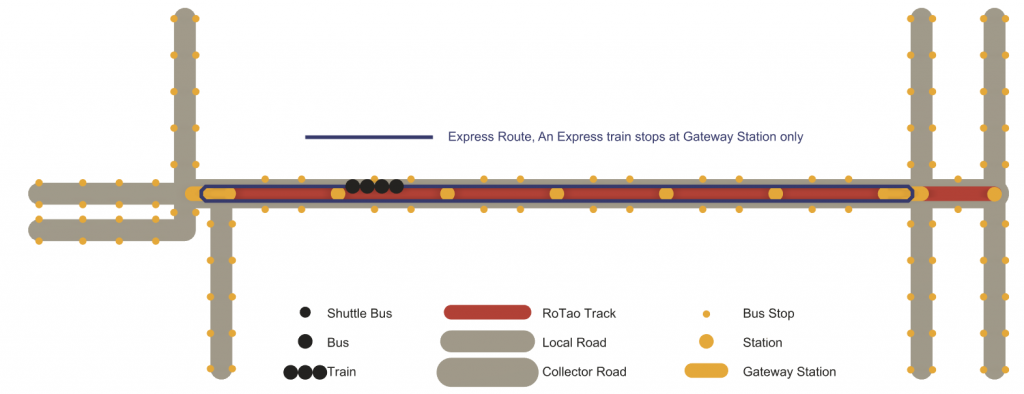
An express train is driven passively by the centralized control system on the Rotao track.
– For on-track operation, it is powered by the tracks. For surface transit, it is converted into individual buses
– It is faster than the rapid train, as it only stops at gateway stations
– It is the fastest vehicle in the Rotao fleet and targets a top speed of 120kph and an average speed of 90kph
– It is best suited for suburban to urban or intercity commuting
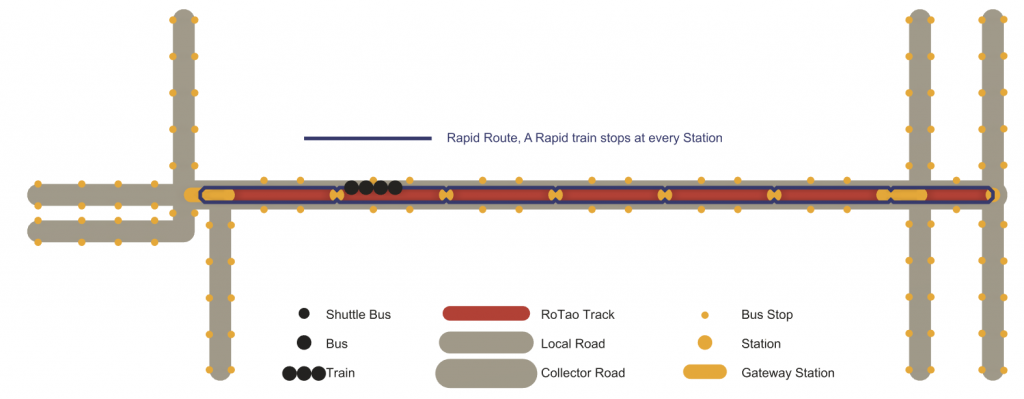
A rapid train is driven passively by the centralized control system on the Rotao track.
– For on-track operation, it is powered by the tracks. For surface transit, it is converted into individual buses
– It stops at every station
– It targets a top speed of 120kph and an average speed of 55kph
– It is best suited for suburban and urban commuting, usually extending the routes of express trains
A collector bus operates on the road under the Rotao track. A local bus operates on roads crossing or close to the Rotao track.
– A collector bus has stops in small increments on the road under the track and elevated stations.
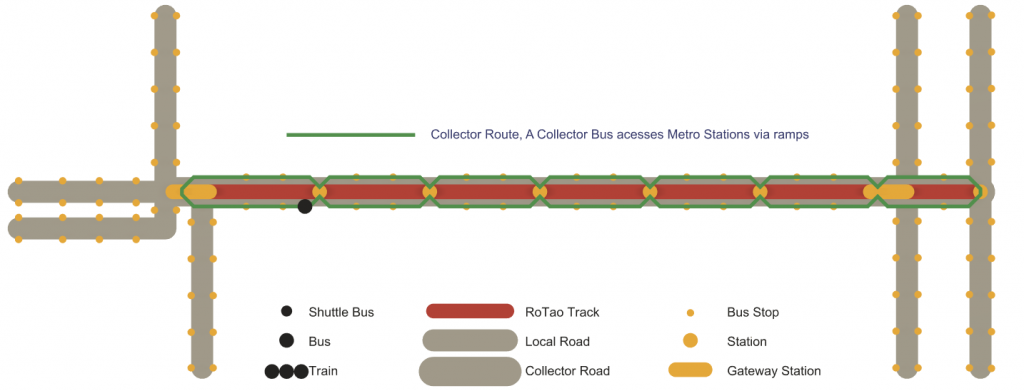
Passengers can be collected to board the train or distributed on the road
– A local bus has stops on roads around the track. The buses merge at elevated stations to form trains.
– It is manually driven
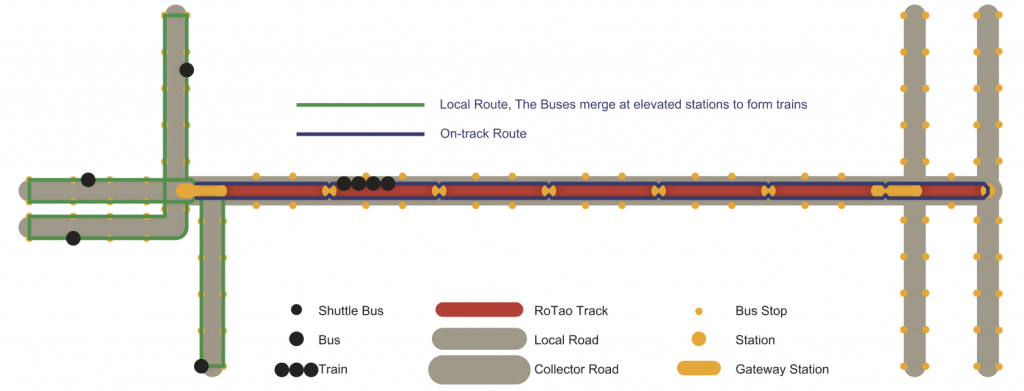
– On the road, it is battery powered. Converted into a train, it is powered by tracks
A shuttle Bus operates on the neighbourhood routes between stations and communities.
– It rises onto the elevated station, where it shares the platform with other buses and trams, then descends onto the road. It is used to collect and distribute passengers.
– It is manually driven; potentially capable of the L5 auto driving
– Although It is way narrower than a normal bus, equipped with an IPASS wheel unit, its axles can be dynamically extended to Rotao standard track width
– It is battery-powered with supplemental charging at elevated stations
No, other than public transit, The Rotao elevated track is also open to other vehicles: (1) large, medium and small cargo vans; (2) large, medium and small passenger vans; (3) cars, SUVs and other passenger vehicles. It should be noted that all vehicles on the track are in passive driving mode.
There are two scenarios where the Rotao rail is used in logistics systems: local and intercity transport. When the vehicle runs on the track, it will be passively driven by a centralized system, powered and charged by a live track. Compared to commercial electric or fossil fuel powered vehicles, it has the following advantages:
– Zero emissions and smaller battery capacity than a regular electric vehicle
– Completely driverless. Passive driving mode allows the vehicle to be driven safely in adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain, fog and/or snow
– Optimized power usage by managing logistics transport during off-peak hours and at night
There are two scenarios for using Rotao rail for private vehicle riders: local(daily commute) transport and intercity(mainly overnight travel) transport. When the vehicle runs on the track, it will be passively driven by a centralized system and powered and charged by a live track. Compared to other EVs or fossil fuel powered vehicles, it has the following advantages:
– Zero emissions and smaller battery capacity than a regular electric vehicle
– Completely driverless. Passive driving mode allows the vehicle to be driven safely in adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain, fog and/or snow
– Compared with L5 automatic driving on the road, in addition to being safer, the driver does not need to be restrained by a seat belt, which enables more freedom to do private work and leisure activities during the journey
– Enabling an overnight-intercity travel method with private vehicles which reduces the travelling cost and saves time. (Enables a cheap and fast method of overnight/intercity transport)
No, the guide rails use different technologies. On a rubber-tired train, the guide rails contact guides to steer the vehicle physically. On the other hand, a Rotao train uses input from sensors to steer the wheels parallel to the rails electronically. However, the guide wheels may contact the rails in certain slippery weather conditions. Thereby, the rail will keep the train on the track.
No, the rubber-tyred metro runs on its dedicated tracks only. It uses turnouts to switch tracks;
Rotao vehicle runs either on a dedicated track or a flat surface. It switches tracks on a flat surface.
Due to the high cost of a turnout, a rubber-tired metro rarely has a separate boarding lane/track; thus, a train cannot pass a parked train; A Rotao train can pass a parked train at a station because every station is equipped with a separate loading lane/track. This feature allows Rotao transit systems to have two levels: Express trains which skip regular stations and stop at large stations, and rapid trains, which stop at every station. This feature optimizes the regular station space and passenger time.
Additionally, two rubber-tyred trains normally require a 1.5 minute headway; thanks to the separated loading track, two Rotao vehicles can keep a headway of 2 seconds or less. This feature ensures the Rotao metro has higher productivity than a regular rubber-tyred metro and can accommodate commercial vehicles and private cars.
The regular elevated rubber-tyred Metro is not commonly used in cold zones. The train can suffer from derailment and switch misalignment due to accumulated snow or ice. In some systems, guide rails are used to power the vehicle. The snow and ice can cause power interruptions. The removal of snow is also difficult. Plowing is hard due to the jagged nature of the track. Salting will damage the track and heating will increase the operating cost.
Rotao metro is suited for inclement weather (snow, rain, and ice). It has an open deck which allows snow, rain and ice through the open section of the deck. The rolling pads are the only flat section that can accumulate snow and ice. They can be cleaned by blowing or plowing and escape through the open section. Electrical heating is also affordable because only the narrow rolling pads require heating.
Rotao track is a dedicated track designed for compatible vehicles. It is mainly elevated on viaducts with a central-wall-beam and open-deck structure. It can be implemented underground as well. Due to the higher cost, underground Rotao transit loses some unique features of the Rotao elevated track:
– Non-walking passenger transfer. shared platforms between all vehicles
– Dedicated parking/loading track, which allows a vehicle to pass a parked vehicle
Bus and metro stop/station spacing greatly impact transit performance. Stop spacing affects both access time and line-haul time, affecting the service’s demand. In general, there is a tradeoff between (a) closely spaced, frequent stops which results in less walking but slower vehicle travel (b) stops spaced further apart, which results in more walking but faster vehicle travel. The capital and operational costs of metro stations are key considerations in planning a metro system.
Our unique station design enables the trains and feeding buses to use the same platform. This ensures that Rotao public traffic can take advantage of the low spacing of bus stops and the long spacing of metro stations. It shortens passenger walking distance and reduces the onboard time. Because feeding buses lift people onto the stations, the requirements for the station itself are lessened, requiring no pedestrian lifts.
The central-wall-beam structure reduces the deck height by up to 2.5 meters compared to the most common box girder structures. The lower deck means that vehicles require less effort or shorter ramps to rise to deck level and descend to ground level.
Each station has a dedicated parking/loading track, which acts as a buffer for vehicles merging and parting from the track.
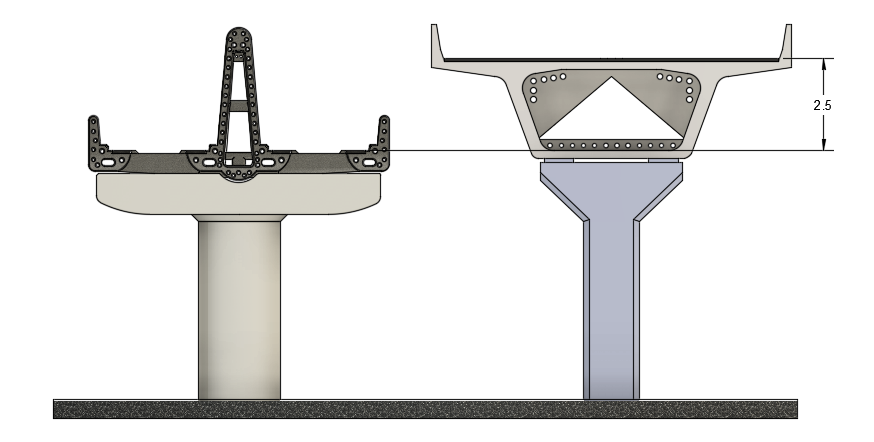
Compared to the most common box girders, the Rotao central-wall-beam open deck structure achieves better vertical space efficiency in two ways: savings in girder height and savings in pier head height.
The span-to-depth ratio is an important bridge design parameter that affects structural behavior and construction costs. The Span-to-depth ratio varies from 12 to 28. Regardless of the effects of construction methods and concrete strength, lower span-to-depth ratios result in less material use and vice versa. The figure above shows that the Rotao girder is deeper than the box girder but still has a lower deck because the girder and the vehicle share vertical space. Also, the Rotao girder has hollow decks. Besides the benefits of aero dynamics and weather resistance, it reduces the dead weight of the deck and pavement. As a result, if the Rotao girder and box girder have the same live load, the Rotao girder viaduct should have a lower deck, lighter structure, and/or longer span.
Firstly, they have different approaches to battery charging.
e-Buses come in ranges from 40km to over 600km depending on battery size. Long range buses can be charged overnight or in the middle of the day between morning and evening service.
Short range buses are designed to be charged on-route using overhead chargers. This allows buses to operate 24 hours a day on route with a short break for charging every hour. This is great for shuttle operations and short routes with frequent service. The downside is the need for expensive chargers located at spots on the route. This limits flexibility but allows buses to have much smaller batteries.
Rotao buses alternatively operate on track or on the road. It is powered and charged by live rails with on track route and battery powered ground route. It has a round trip battery of around 80 KM range or 110 KWH.
Additionally, the Rot bus is all wheel steerable. the Rotao bus has a smaller turn radius than a front wheel steering bus, Also, the Rotao bus can move to the side, which benefits parallel parking. Working with cameras and sensors, the Rotao bus parks itself close to the curb faster and safer than manual parking.
Moreover, compared to the 2 axle/6 wheel setup of a regular e-bus, the Rotao bus has 4 axles and 8 wheels. This means the bus has more support from the ground. More supporting points make the bus more tolerant of bumpy roads. And leads to a more smooth and comfortable ride.